Shockwave Therapy and Heel Pain ESWT (Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy) is a non-invasive surgical procedure that involves sound waves. The sound waves are utilised to stimulate the […]
A Brief Look at Flexible Flatfoot
A Brief Look at Flexible Flatfoot

A Brief Look at Flexible Flatfoot
Flatfoot is a condition that is characterised by deformity. There are different kinds of Flatfoot Deformities but one of the most common is Flexible Flatfoot, which typically begins in childhood or adolescence and continues into adulthood. The condition generally occurs in both feet and then progresses in its severity throughout most of the adult years. As the condition progresses the tendons, ligaments and the soft tissues of the arch can tear or stretch and become inflamed. It is referred to as flexible since even though the weight-bearing foot is flat while standing, the arch returns to its original shape while not standing.
Symptoms associated with flexible flatfoot
The symptoms of flexible flatfoot vary from patient to patient and include the following:
- Lower back, knee or hip pain
- General fatigue or aching in the leg or foot
- Pain along the patient’s shin bone
- Over-pronation of the ankle or “rolled-in” ankle
- Pain in the arch, heel, ankle, or the area just along the outside of the patient’s foot
Flexible Flatfoot Diagnosis
Diagnosis of flexible flatfoot, will first involve examination of the foot and how it functions when the patient is trying to sit and stand. The overall severity of the condition is determined by X-rays. Sometimes a patient might have flexible flatfoot without any associated symptoms. In such cases, the specialist will try and determine what the patient might experience in the future.
Treatment of Flexible Flatfoot
There are a number of non-surgical treatment options for managing Flexible Flat Foot, such as:
Activity modification: The patient should minimize activities that cause pain and strictly avoid prolonged standing and walking so that the arches may have rest.
Immobilization: In certain instances, it may become necessary to make use of a walking cast. The specialist may also recommend complete avoidance of weight bearing.
Orthotic devices: The surgeon can present the patient with customized orthotic devices so that additional support is provided for the arches.
Weight loss: Having too much additional weight on the arches may actually aggravate the symptoms. If the patient is overweight, he or she will likely benefit from losing weight.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy modalities like ultrasound therapy can be used for providing temporary relief.
Medications: The surgeon may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen to help reduce the pain and inflammation.
AFO or Ankle Foot Orthoses devices: The specialist may recommend some advanced bracing for modifying walking and providing support to the arches.
Shoe modifications: If the patient is not already doing so, modifying their shoes to ensure appropriate arch support may be of benefit.
If the above procedures fail to resolve the pain associated with flexible flatfoot, surgery may become necessary. The type of surgery that is carried out will depend on the extent of the deformity, as indicated by x-ray findings, the age of the patient, activity levels and various other factors
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
Categories
Related Blogs
Thoughts and advice on foot health care from the Podogo team.
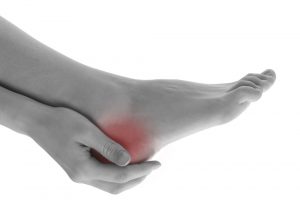
When Is Surgery Needed for Heel Pain?
When Is Surgery Needed for Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common issue that can cause pain whilst standing or walking. There are many cases where […]
When is Surgery needed for a Flat Foot Issue?
When is Surgery needed for a Flat Foot Issue? Flat foot surgery is intended to correct the present alignment of your feet, ease any pain you […]
Understanding Hammer Toe
Understanding Hammer Toe Hammer toe affects your second, fourth, and third toes which causes them to bend at the middle joint, making them appear like a […]
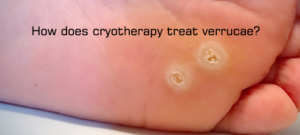
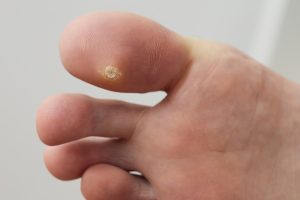
How Does Cryotherapy Treat Verrucae?
How Does Cryotherapy Treat Verrucae? Verrucae, referred to as plantar warts, are rough and small growths that usually appear on the soles of your feet. These […]
Understanding Flat Feet
Understanding Flat Feet Flat feet, also referred to as pes planus, indicate a condition where the arches of your feet have collapsed, this can become very […]
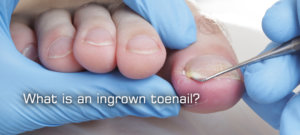
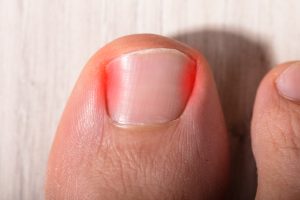
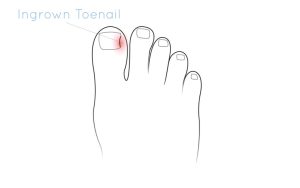
What is an ingrown toenail?
What is an ingrown toenail? An ingrown toenail develops when the sides of the toenail cut in to the skin. The body treats the nail as […]
Stepping with Comfort: A Guide to Common Foot Conditions
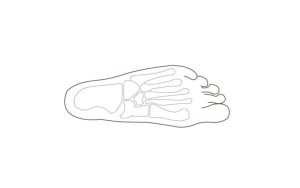
Stepping with Comfort: A Guide to Common Foot Conditions There are 26 bones in a human foot, with 33 joints and a minimum of 100 muscles, […]
Returning to Sports After an Achilles Tendon Rupture
Returning to Sports After an Achilles Tendon Rupture An ATR (Achilles tendon rupture) is a rather common injury among individuals who tend to be physically active. […]
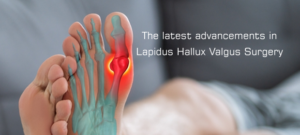
The Latest Advancements in Lapidus Hallux Valgus Surgery
The Latest Advancements in Lapidus Hallux Valgus Surgery Correcting hallux valgus is one of the most common procedures undertaken by foot and ankle specialists. There have […]
What is a Podiatrist and their training
What is a Podiatrist and their training [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] When it comes to taking care of our bodies, our feet often get overlooked. Enter the podiatrist, […]
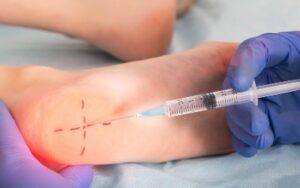
Understanding Steroid Injections: A Podiatrist’s Guide
Understanding Steroid Injections: A Podiatrist’s Guide [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] What are Steroid Injections? Steroid injections are commonly used in the field of podiatry to alleviate pain and […]
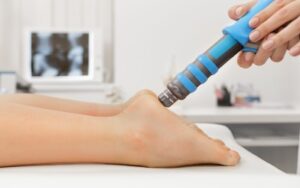
The Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Podiatry Patients
The Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Podiatry Patients [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] What is Shockwave Therapy? Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive and highly effective treatment method for various […]
Treating Sports Injuries: Shockwave Therapy vs. Steroid Injections
Treating Sports Injuries: Shockwave Therapy vs. Steroid Injections [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] Sports Injuries Sports injuries are a common occurrence among athletes, weekend footballers and beginner joggers. Sports […]
Ankle Sprain or Fracture
Ankle Sprains and Fractures [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] Ankle sprains and fractures are common injuries that can effect both very active and sedentary people. At Podogo Foot Clinic, […]
Ingrown Toenail Remedies You Can Do at Home
Ingrown Toenail Remedies You Can Do at Home [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] Ingrown nails whether on the fingers or toes develop when the side of the nail starts […]
Treatment for verrucae and warts
Treatment for verrucae and warts [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] Verrucas and warts are very common and are contagious so you should be careful when walking barefoot. They are […]
What is biomechanical gait assessment?
What is biomechanical gait assessment? [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] A gait analysis and biomechanical assessment are two different types of assessment, they are both ways of examining how […]
Heel pain and plantar fasciitis exercises
Heel pain and plantar fasciitis exercises [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] There are many causes of heel pain but one of the biggest causes is plantar fasciitis which affects […]
Common Questions About Plantar Fasciitis
Common Questions About Plantar Fasciitis [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] What is the main cause of plantar fasciitis? It is generally classed as an overuse injury that gradually worsens. […]
Common Questions About Verruca
Common Question about Verrucae [betterdocs_search_form placeholder=”Search”] Do verruca go away on their own? They can go away on their own but there is no guarantee of […]
Surgery for Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown Toenail Surgery | All You Need to Know About it What is an ingrown toenail? An ingrown toenail is when part of the toenail has broken or pierced the surrounding skin. What causes an ingrown toenail? They are often caused by malcutting, leaving a shard down the side of...
Metatarsalgia – Pain in the ball of the foot when walking
What causes pain in the ball of the foot when walking? There are a number of possible causes for this. The ‘balls’ of the feet are technically, the metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints). Pain in this area can mean that one of these joints, or the structures or surrounding structures of...
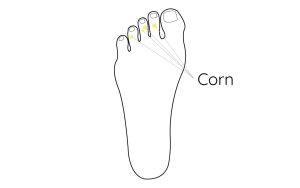
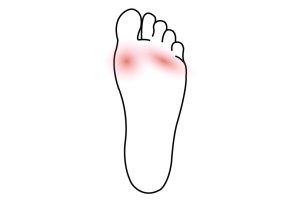
What is a Foot Corn?
What is a Foot Corn? Appearance A corn is a bump of hard skin on the foot. They typically appear as a raised hard, yellowish patch of skin that is often tender to touch and painful when walking or wearing shoes. A corn is not normally a serious health condition....
What is the pain in the ball of my foot?
What is the pain in the ball of my foot? It is quite common to feel pain and inflammation around the balls of the feet. Podiatrists refer to these symptoms as Metatarsalgia, although this is not a condition in itself. The balls of the feet are the slightly padded areas...
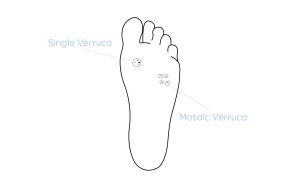
The Best Verruca Treatments
The Best Verruca Treatments What is a Verruca? A Verruca is a small lump of hard skin, also known as a plantar wart, that grows on the sole of the foot. Verrucae typically appear as a small black dot beneath the surface of the skin with hard skin growing on...
Treating Ingrown Toenails
Treating Ingrown Toenails What is an ingrown toenail Ingrown toenails occur when the nail starts to pierce the skin and soft flesh surrounding it. This is quite common and typically affects the big toes. Often this condition is caused by: Wearing tight shoes that push the toes together Cutting your...
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis The plantar fascia is a structure under the foot that connects the heel to the metatarsophalangeal joints (MTPJs) or commonly called the ‘balls of the feet’. Plantar fasciitis refers to inflammation of the fascia that produces symptoms. The typical location of symptoms are where the fascia inserts into...
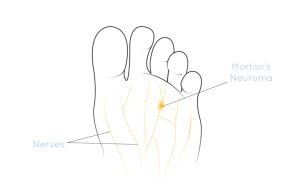
What Is a Morton’s Neuroma?
What Is a Morton’s Neuroma? A Morton’s Neuroma is a thickened, damaged or irritated nerve between your toes. This can cause pain, discomfort or restriction in footwear and may require specialist treatment. A Morton’s neuroma is found between the third and fourth webbing space of the foot but neuromas can...
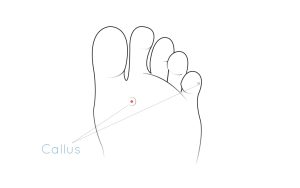
Preventing Callus and Corn formation
Preventing Callus and Corn formation Callus and corns are extremely common on our feet. A thin layer of flexible callus is a healthy protective barrier of the skin. Corns however do not have any benefit and can be immensely painful. Here is information and advice on these two common complaints....
Verrucae
Verrucae are warts on the foot and are caused by a virus. When present under the foot they can be very painful to walk on, particularly if under high pressure areas. The virus itself does not cause pain, but the hard skin it develops does. Verrucae are contagious and spread...
Orthotics
Orthotics Orthotics are commonly known as insoles and are worn inside shoes. They ultimately change forces on your foot and can be used for a variety of reasons. Thin flat cushioned insoles available from a number of high street shops can improve general comfort. However, for people with foot complaints...
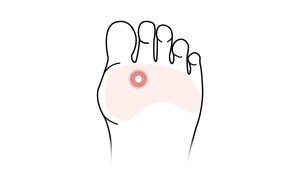
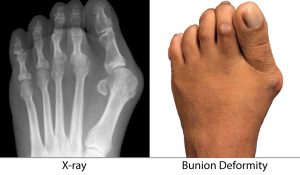
National Bunion Day
National Bunion Day A bunion is a deformity of the foot involving the big toe joint. This is often painful and can cause a number of secondary problems. The medical term for bunion is ‘hallux valgus’, and it affects around 23% of adults – women more than men. The big...
Easter walks
Easter Walks After a period of cold and dark winter weather, the temperature is rising. Trees are sprouting fresh green leaves, and flowers begin to bloom and add colour to the landscape. This is a pleasant invitation to explore outside. You may be planning a city break away or trip...
Valentines Day and wearing heels
Valentines Day and wearing heels As you may be planning to wear heels this Valentine’s Day, here is some advice to consider from a foot and ankle specialist. All feet and people are unique and will therefore be prone to different types of problems and symptoms. However, the main factors...
Preparing for the London Marathon
Preparing For The London Marathon Preparing for the London Marathon is different for each individual. For some, running the marathon will be the first time they run this distance. For others, it may be a frequent event alongside triathlons and ultramarathons. The closer you are to the later group, the...
New Year’s Resolutions
New Year’s Resolutions Most people make New Year’s resolutions, and the classic one is ‘to keep fit and get in shape’. Based on clinical experience, I see many patients in late January and February due injuries as a direct result of their resolutions. This is not a good start to...
Common Foot Issues & Foot Treatment
Common Foot Issues & Foot Treatment Athlete’s Foot: Athlete’s foot is one of the most common foot related issues that people may suffer from. The foot treatment for this particular issue is rather simple. You just keep his feet dry and clean at all times, as well as use a...
Planters Foot: An Inflammation of A Ligament In Your Foot
Planters Foot: An Inflammation of A Ligament In Your Foot In medical terminology planters foot is known as plantar fasciitis. It is basically an inflammation of a ligament in your foot named the plantar fascia.
What You Need to Know About Foot Injuries
What You Need to Know About Foot Injuries Each foot in your body has 26 bones, 33 joints, and at least 100 tendons, ligaments, and muscles. This is the reason why foot injuries are so common
Sore Feet: Pain & Discomfort in Your Feet
Sore Feet: Pain & Discomfort in Your Feet The term sore feet means what it says – pain and discomfort in your feet. There are several symptoms of sore feet that may be mentioned as below: Hammer toe Discolored skin Bunions Corns Calluses Heel pain Arch pain If you have...
How To Find The Right Foot Care Centre
How To Find The Right Foot Care Centre Though we generally associate foot pain or injuries with athletes, we should not fail to acknowledge the fact that they can be experienced by anyone. A well equipped foot care centre should ideally provide all the following treatment options: Bunion Treatment Heel...
How to Protect Your Ankle from Sports Related Injuries
How to Protect Your Ankle from Sports Related Injuries If you are into sports and fitness activities, then you will be well aware of the fact that ankle injuries are quite common and you may know how to avoid them.
Hammer Toe Exercises That You Can Easily Do At Home
Hammer Toe Exercises That You Can Easily Do At Home If you have been diagnosed with a hammer toe, it is important that you perform exercises that will help you to repair and restore the feeling, shape and functionality of the toes.
General Orthotics: Dispelling Myths about Orthotics
General Orthotics: Dispelling Myths about Orthotics Orthotics are basically insoles that are meant to improve foot posture by providing form and structure. Manufacturing bespoke orthotics is a highly technical process. In spite of their proven efficacy, it is a common belief that they do not work. In the course of...
Rare or Uncommon Foot Conditions Never be Ignored
Rare or Uncommon Foot Conditions Never be Ignored Foot problems may appear simple but they should never be ignored as they can often become very serious. In most cases, foot conditions are caused by simple factors which can be easily identified with standard diagnostic procedures. However, there can also be...
Golf Injuries – What You Need To Know
Golf Injuries – What You Need To Know Considering the less-aggressive nature of the sport, we don’t really associate golf with injuries. However – quite contrary to popular belief, golfers are prone to foot injuries – just like cricketers or footballers. Golf is one of the popular sports played widely...
A Few Things That You Need to Know About Foot Specialists
A Few Things That You Need to Know About Foot Specialists A Foot Specialist is also referred to as a Podiatrist. They are basically physicians who specialize in problems related to the foot and ankle. People often do not know much or anything about Podiatrists until they have to visit...
Sesamoid Bones & Treatment for Sesamoid Pains
Sesamoid Bones & Treatment for Sesamoid Pains The human body consists of more than 200 bones. Most of these bones are connected to one other at the joints. However, there are some bones that do not share any connections with other bones. Instead, these bones are connected to the tendons...
Tips to Find the Right Podiatrists
Tips to Find the Right Podiatrists Podiatrists are healthcare professionals who might play a very important role in your lives by diagnosing, treating and rehabilitating common foot conditions including: Hammer Toes Bunion Flat Foot Heel Pain Ankle Arthritis Gait Analysis Smart Toe Implant Ankle Instability Achilles Tendon Others Podiatrists: Are...